- What is hyperpigmentation and why do dark spots appear? - February 18, 2026
- Hives: causes and treatment, what usually works? - February 17, 2026
- Forxiga vs Jardiance: what are the differences - February 14, 2026
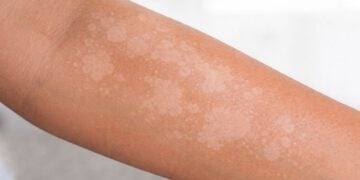
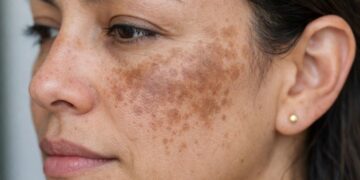
Hyperpigmentation is the darkening of areas of skin due to an increase in pigment, primarily melanin. It usually appears as spots or patches darker than the usual skin tone and, in most cases, is not dangerous, although its appearance can be a concern.
What does hyperpigmentation mean?
This means that certain areas of the skin produce or accumulate more pigment than the surrounding skin, for various reasons. It can be localized (a specific spot) or more extensive, and its appearance helps determine whether it is superficial, deeper, or linked to a clear trigger.
Hyperpigmentation: most frequent causes
The most common cause is sun exposure, because the skin responds by producing more melanin, and over time spots can appear. Genetic factors also play a role, and in some people, hormonal changes.
Another common cause is post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, which appears after acne, eczema, irritations, injuries, or skin procedures. Some medications and substances can also cause changes in skin color, especially if photosensitivity is present.
| Frequent type | Typical track |
|---|---|
| Melasma | Face, symmetrical |
| Solar lentigines | Exposed areas |
| Post-inflammatory | After acne |
| Acanthosis nigricans | Folds, velvety |
Hyperpigmentation: when to consult a doctor
It's advisable to consult a doctor if you notice new spots you don't recognize or if there are skin changes that concern you, even if they don't hurt. This is especially important if the lesions change significantly or are accompanied by other general symptoms that don't fit with a purely cosmetic issue.
The doctor usually guides the diagnosis with the patient's history (when it started, sun exposure, medications, previous inflammation) and a physical examination. In some cases, tests are ordered to rule out underlying causes when the pattern suggests it's not just a sunspot.
Hyperpigmentation: management and prevention options
For facial patches such as melasma, a dermatologist often combines sun protection with depigmenting treatments depending on the case. Some actives like hydroquinone can cause problems if used for a long time or without supervision, so self-treatment is not advisable.
Daily sun protection is key to preventing dark spots from worsening and reducing recurrences, especially in sun-exposed areas. It also helps to avoid scratching or picking at lesions and to treat irritated skin gently, as repeated inflammation can leave more residual pigment.
This text is for informational purposes only and does not replace medical advice. Always check the package leaflet and follow the instructions of your doctor or pharmacist.